ABOARD THE USS THEODORE ROOSEVELT — The U.S. Navy showcased what one senior officer said was the “sausage being made during test and evaluation” this past weekend as one of its Unmanned Combat Air System (UCAS) Demonstrators experienced an anomaly during a media tour aboard the USS Theodore Roosevelt.
The anomaly was resolved quickly with a 90-min. reboot of the Northrop Grumman-built air vehicle, after which operators conducted a catapult launch and wave-off procedure before an arrested landing back on deck.
The service is two days into an “at-sea” period for a newly approved round of carrier trials designed to test the single-engine, stealthy X-47B’s performance in off-nominal conditions, such as high winds or off-axis winds over the carrier deck. Ultimately, officials are looking to evaluate performance at winds of 28-36 kt.
Read more here.
The Northrop Grumman-built aircraft landed at 12:23 p.m. Eastern time while the aircraft carrier was under way off the coast of Virginia, and marks the latest and most significant achievement for the program during carrier sea trials, which began in May.
“Today’s historic carrier landing and our operations aboard USS George H.W. Bush show, beyond a shadow of a doubt, that tailless unmanned aircraft can integrate seamlessly and operate safely from an aircraft carrier at sea,” said Capt. Jaime Engdahl, Navy UCAS program manager. “Beyond X-47B, this moment in history was made possible by an extremely disciplined and dedicated government-industry team that took a brand new unmanned combat air system from initial concept to highly successful demonstration in one of the most demanding operating environments in the world.”
Read the full news release here.
Program Overview:
In August 2007, the U.S. Navy selected Northrop Grumman as the prime contractor for the Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstration (UCAS-D) program. The program will demonstrate the first-ever carrier launches and recoveries, and autonomous aerial refueling by an autonomous, low-observable-representative unmanned aircraft.
To date, Northrop Grumman has designed and built two tailless, fighter-sized unmanned aircraft designated the X-47B. The company will use these aircraft to demonstrate two “firsts” for unmanned jet-powered aviation: autonomous carrier operations – including launch, recovery, and deck handling – and autonomous aerial refueling using both the U.S. Air Force “boom-receptacle” and Navy “probe and drogue” methods.
First flight of Air Vehicle-1 (AV-1) occurred on Feb. 4, 2011 with a flight test envelope expansion program planned to conclude in late 2011. First flight of AV-2 is also planned for 2011. Over the next two years, the program will conduct additional flights and carrier suitability tests that will lead to the completion of the Navy’s carrier launch and recovery objectives by 2013. Successful at-sea trials will set the stage for potential follow-on acquisition programs for carrier based unmanned systems.
The X-47B is a tailless, strike fighter-sized unmanned system currently under development by Northrop Grumman as part of the U.S. Navy’s Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstration (UCAS-D) program. Under a contract awarded in 2007, the company has designed, developed and is currently producing two X-47B aircraft. In the 2013 timeframe, these aircraft will be used to demonstrate the first carrier-based launches and recoveries by an autonomous, low-observable relevant unmanned aircraft. The UCAS-D program will also be used to mature relevant carrier landing and integration technologies, and to demonstrate autonomous aerial refueling by the X-47B aircraft.
Foundation for the Future:
UCAS-D is designed to help the U.S. Navy explore the future of unmanned carrier aviation. A successful UCAS-D flight test program, including a series of successful carrier-based launches and recoveries, will help set the stage for the development of a more permanent, carrier-based fleet of unmanned aircraft.
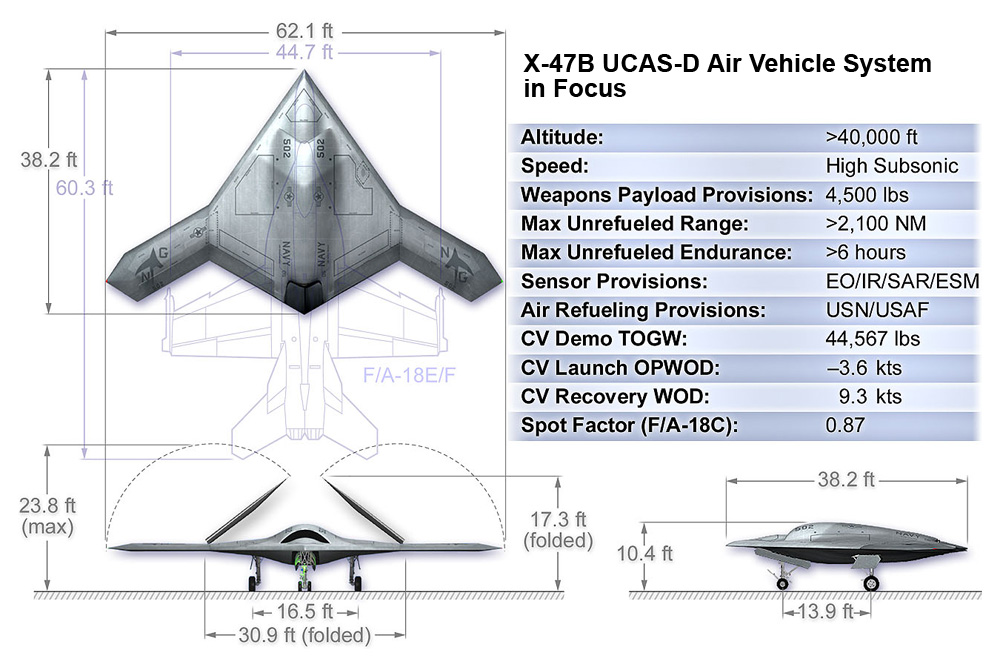
X-47B Specifications
• Wingspan: 62.1 ft (collapsible wing span 30.9 ft)
• Length: 38.2 ft
• Altitude: 40,000 feet
• Range : 2,100 nm
• Top Speed: High subsonic
• Power Plant: Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-220U
System Provisions
• Autonomous Aerial Refueling Probe & Drogue (USN)
• Boom Receptacle (USAF)
• Weapons Bays 4,500 pounds
• Sensors EO/IR/SAR/ISAR/GMTI/MMTI/ESM
Source: Northrop Grumman
Recent News: U.S. Navy Restarts X-47B Trials Aboard Roosevelt Carrier – November 12, 2013
Northrop Grumman, U.S. Navy Complete First Arrested Landing of X47B on an Aircraft Carrier – July 10th, 2013
Navy Launches First Ever Drone From Carrier – May 14th, 2013
U.S. Navy Conducts First Fly-in Arrested Landing for the X-47B – May 6th, 2013
X-47B completes historic at-sea period aboard Truman – December 18, 2012
Northrop Grumman, U.S. Navy Demonstrate Precision, Wireless Ground Handling of X-47B Unmanned Aircraft -November 15, 2012
Northrop Grumman, U.S. Navy Conduct First East Coast Flight of X-47B Autonomous Unmanned Aircraft – July 30, 2012
U.S. Navy, Northrop Grumman Complete X-47B Flight Testing at Edwards Air Force Base, Move Second Unmanned Aircraft to East Coast – June 14, 2012
A Day in the Life of X-47B UCAS – June 14, 2012 (VIDEO)
U.S. Navy Test Autonomous Aerial Refueling for Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstration – January 26, 2012
Expansion of Fleet Adds Momentum, Flexibility to Flight Test Program – November 28,2011
Gear Up! U.S. Navy/Northrop Grumman X-47B Demonstrator Flies in Cruise Mode for First Time – October 10, 2011
U.S. Navy, Northrop Grumman Successfully Test Systems Required to Operate X-47B Unmanned System From an Aircraft Carrier – July 5, 2011



